What is a Mooring of Ship?
1:- Introduction to Mooring Operation
Have you ever wondered how ships are parked or held fast at a place? Unlike cars and other vehicles, ships do not have wheels and brakes to come to a halt, then how are ships stopped at a place while doing the cargo operation and what are the things used to hold fast a hundred thousand tons of ship at a place?
You will be surprised to know that the thing holding such a giant ship in place is a tool that can be found in any household: A rope and the procedure of putting the ropes in a place is called a mooring operation. Do not confuse the mooring operation of the ship with the anchoring of the ship, they are both completely different.
To learn about the anchoring of a ship: CLICK HERE.
2:- Mooring Ropes for Mooring Operation of Ship
- Mooring ropes (also called mooring lines) are ropes, cables, or chains used to tie a ship to a dock, buoy, or anchor, keeping it stable and preventing it from drifting due to wind, waves, or currents. They are very important for the ship’s safety when it’s not moving, protecting both the crew and cargo.
- Different materials are used based on the ship’s needs:
- Synthetic: Nylon, polyester, and polypropylene-strong and long-lasting.
- Natural Fibers: Manila, sisal, and cotton-eco-friendly but wear out faster.
- Metal: Steel wire ropes-extremely strong, used for large ships or harsh conditions.
3:- Mooring Equipment on Ship
There are 5 basic components and machinery used for mooring operations:
- Mooring Lines
- Mooring Winches
- Diving Systems
- Vessel Fitting
- Fenders
4.1:- Mooring Winches?
- Mooring winches are essential components in any mooring system, designed to manage and control the tension in mooring lines. Historically, manual winches were common, but modern vessels utilize powered winches made of high-grade steel and advanced materials for durability and efficiency. The main requirements of mooring winches are high load capacity, reliability, and precise control. They handle the forces transmitted from the mooring lines as they adjust to static and dynamic loads influenced by environmental factors like waves, wind, and current.
- The net effect on mooring winches is significant due to the constant load and variable motion forces. Therefore, these winches are designed with precise braking systems and load sensors to maintain safe line tension. Electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic systems are used based on the vessel type and mooring arrangement. Winches for larger vessels are generally high-capacity and robust, while smaller vessels may use lighter, more flexible winch systems to accommodate the varying motion dynamics encountered.
4.2:- Mooring Ropes
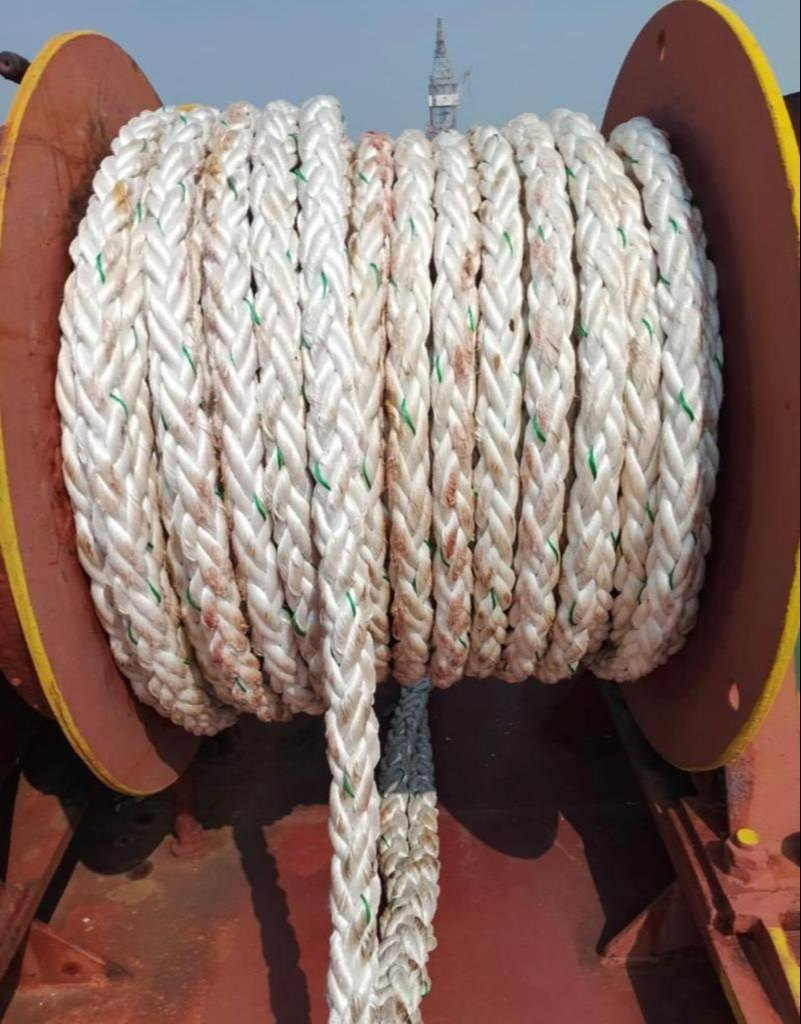

- Mooring ropes are made from synthetic fibers or steel wire, designed to balance elasticity and strength for effective vessel mooring. Various types of ropes, like breast lines and spring lines, serve specific functions to control the ship’s positioning and movement. Breast lines stabilize the vessel laterally, while spring lines manage forward and aft motion, preventing drifting due to environmental forces such as tides, currents, and wind.
- To ensure the durability and safety of mooring ropes, regular inspection and maintenance are essential. Routine checks help identify wear, fraying, or damage, allowing timely replacement or repair. Proper care of mooring ropes ensures the mooring system remains efficient and reliable, minimizing risks during vessel docking and berthing operations.
4.3:- Fairleads
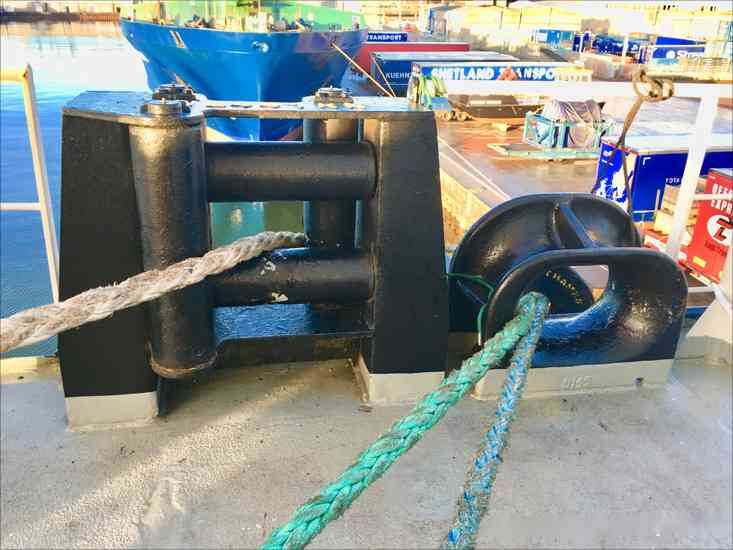

- Fairleads help guide mooring lines smoothly from the ship’s deck to the shore, preventing damage and chafing during direction changes. They come in different types, like roller and closed fairleads, to suit various line handling needs. Made from strong materials like steel, fairleads ensure durability and long-lasting performance.
4.4:- Bollards for Ship
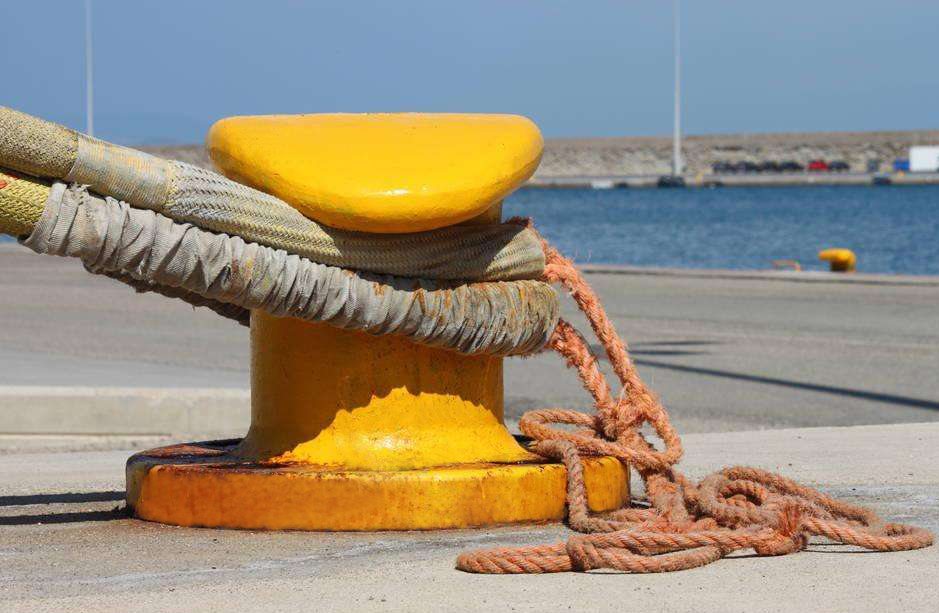

- Bollards are strong, fixed posts on docks designed to secure mooring lines and keep vessels stable. They come in different shapes, like single, double, or T-shaped, to fit various mooring line types and sizes, ensuring flexibility and secure docking for different vessels.
5:- Mooring Lines Arrangement
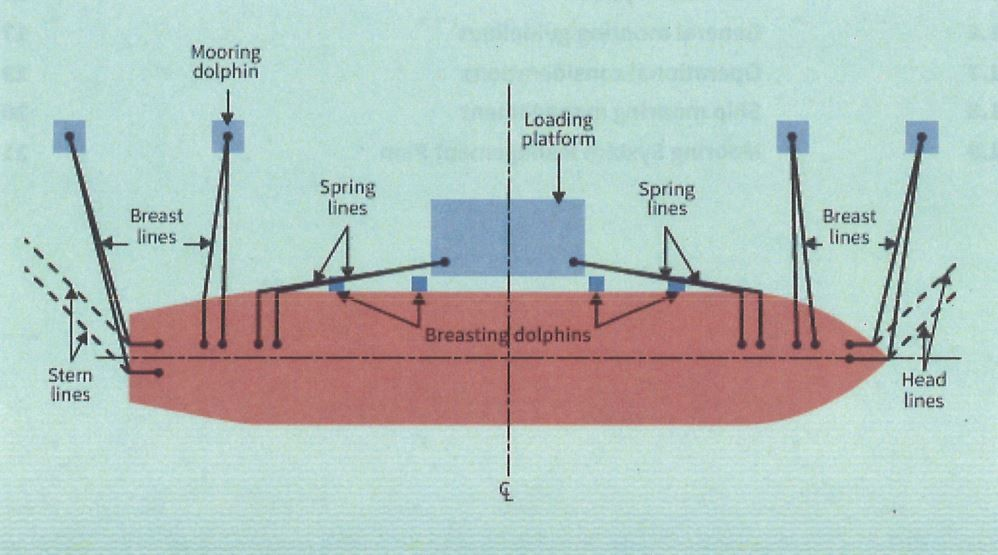
Mooring line arrangements are critical for securely holding a vessel in place at a berth, countering forces like wind, current, and tides. The arrangement and positioning of these lines are tailored to the vessel’s size, shape, and mooring environment, ensuring stability and safety.
- Head Lines
- Position: From the bow of the ship extending forward to the dock.
- Function: Prevents the vessel from moving aft (backward) and stabilizes the bow.
- Stern Lines
- Position: From the stern (rear) of the ship extending aft to the dock.
- Function: Prevents the vessel from moving forward and stabilizes the stern.
- Breast Lines
- Position: Extends perpendicular from the vessel’s side (midship) to the dock.
- Function: Holds the ship close to the dock, minimizing lateral movement away from or towards the dock.
- Spring Lines
- Position: Diagonally positioned from the bow or stern to the dock, running parallel to the ship’s length.
- Forward Spring Lines: Extend from the bow to a point further aft on the dock.
- Aft Spring Lines: Extend from the stern to a point further forward on the dock.
- Position: Diagonally positioned from the bow or stern to the dock, running parallel to the ship’s length.
- Cross and Additional Lines
- Position: Used when additional securing points are needed, often crossing over other lines.
- Function: Provides extra stability, especially in areas with high currents or tidal fluctuations.
6:- Most Common Mooring Methods
The mooring process must withstand forces like wind, currents, tides, and waves. Here are the most common mooring methods:
Single Point or Single Buoy Mooring
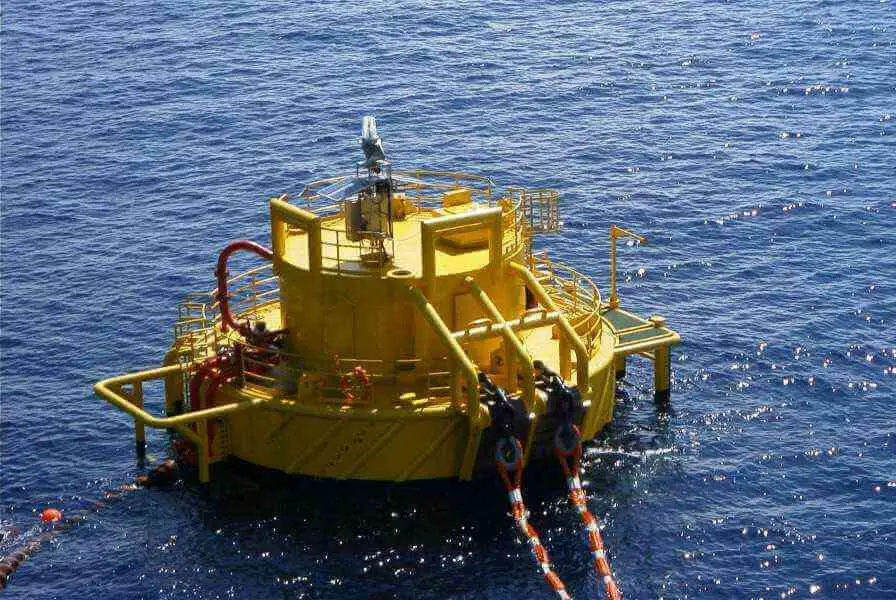

- This method uses a floating dock or buoy outside the port, mainly for liquid or gaseous cargo.
- The ship is tied to a buoy with one or two chains attached to the bow. It’s best used in calm weather with low waves and wind.
Conventional or Multi-Buoy Mooring:
- The ship’s bow is secured with two anchors, while the stern is tied to a buoy.
- The ship approaches the mooring position at a 90-degree angle. The starboard anchor is dropped as the ship moves forward, and when it stops, the port anchor is dropped, aligning the ship with the buoys.
Baltic Mooring:
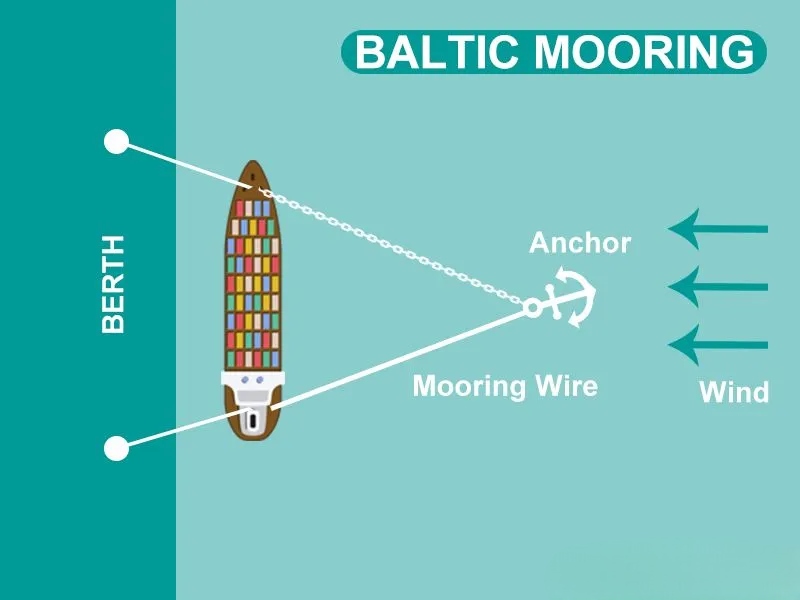
- Used in strong winds and when tugboats are unavailable, this method involves using the ship’s anchor and onboard cables to reduce the impact on a dock that can’t withstand heavy impact. The ship is berthed lengthwise to the dock.
Mediterranean Mooring:
- The ship is moored perpendicular to the dock, with the stern parallel to the jetty.
- Mediterranean mooring is used when dock space is limited or when there is a stern ramp for loading (e.g., on car carriers).
7:- Difference between Mooring and Anchoring
| Anchoring | Mooring |
| Involves lowering an anchor to the seabed to secure the vessel. | Mooring securing the vessel to a fixed structure like a dock, pier, or buoy. |
| Anchoring is used for temporary positioning, especially in deep waters. | Mooring is commonly used for longer-term stays near shore or in a harbor. |
| Stability is provided by the anchor gripping the seabed. | Stability is achieved through ropes, chains, or cables attached to fixed points. |
8:- Conclusion
In conclusion, mooring operations play a critical role in shipping by ensuring that ships are properly secured to withstand a variety of factors, including waves, tides, wind, and currents.
The selection of mooring lines and winches, which must be appropriate for the ship’s size, the surrounding conditions, and the particular activity being carried out, determines how successful mooring is.
Disclaimer :- The opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author and may not necessarily reflect those of Merchant Navy Decoded. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information provided and disclaim any responsibility for it. Data and visuals used are sourced from publicly available information and may not be authenticated by any regulatory body. Reviews and comments appearing on our blogs represent the opinions of individuals and do not necessarily reflect the views of Merchant Navy Decoded. We are not responsible for any loss or damage resulting from reliance on these reviews or comments.
Reproduction, copying, sharing, or use of the article or images in any form is strictly prohibited without prior permission from both the author and Merchant Navy Decoded.


