Types of Sensors Used on Ships: Increasing Ship Efficiency and Safety
1:- Sensors Used Onboard
In the expansive world of maritime operations, sensors play a pivotal role in ensuring a vessel’s performance, navigation, safety, and regulatory compliance.
Sensors used on ships are integral for monitoring a wide range of operational parameters, providing data that informs decisions both on board and remotely by shipping companies.
Merchant Navy Decoded will help you explore essential types of sensors used on ships.
2:- Speed Log on Ship
A speed log is a device that measures the vessel’s speed through water, providing essential data for navigation and performance calculations. The speed log sensor is crucial for determining the vessel’s fuel consumption efficiency and evaluating its performance against environmental conditions.
2.1:- How does Speed Log Work?
The speed log emits acoustic signals that bounce off particles in the water. The time it takes for these signals to return allows the device to calculate the vessel’s speed.
Speed Log accuracy can be affected by environmental factors such as water clarity, aeration, and sea state. Example: In turbid or dirty water, the reflection quality decreases, which can lead to inaccuracy in the speed log output.
- The benefit of Using Speed Log
- Speed Log sensor helps to optimize fuel efficiency by providing real-time speed data.
- Speed Log sensor ensures accurate performance and time assessments during voyages.
3:- Echo Sounder
The echo sounder is used for measuring water depth, especially in shallow or confined waters.
Echo sounders are essential for safe navigation as they provide real-time data on the distance between the vessel’s hull and the seabed, reducing the risk of grounding.
3.1:- How Does an Echo Sounder Work?
Echo sounders send out sound waves that bounce off the seabed and return to the sensor. The device calculates the depth based on the time it takes for the sound wave to return.
It is essential to set the frequency of the sounder appropriately, with typical values ranging from 28 to 210 kHz. Higher frequencies are used for shallow water and lower frequencies for deeper water.
- Benefits of Using an Echo Sounder
- Echo Sounder enhances safety by preventing accidental groundings.
- Echo Sounder provides valuable data for navigation in shallow waters and port approaches.
- Echo Sounder used during dredging operations to ensure sufficient depth for vessels.
4:- RPM and Torque Meter (Tachometer)
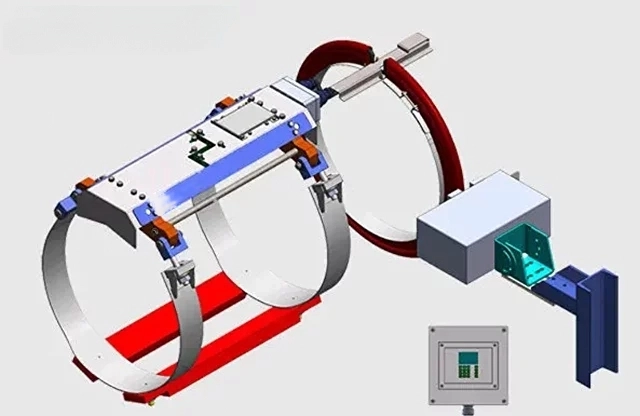
RPM (Revolutions Per Minute) and torque meters are essential for monitoring the performance of the ship’s propulsion system.
RPM Meter or tachometer measures the rotational speed of the engine and the torque generated on the propeller shaft, respectively.
4.1:- How Does RPM and Torque Meter (Tachometer) Work?
The torque meter uses strain gauges mounted on the propeller shaft to measure the amount of force applied. These gauges detect the slight deformations in the shaft as it turns, and this data is used to calculate torque.
RPM meters measure the speed of the propeller shaft, usually with a laser-based system, ensuring the vessel operates at optimal efficiency.
5:- Shaft Motor Sensor
The shaft motor sensor measures the power output of the ship’s shaft motor, which transfers electricity to the propulsion system.
On modern vessels, this sensor plays a vital role in ensuring the shaft motor operates efficiently, particularly in conjunction with waste heat recovery systems.
5.1:- How Does Shaft Motor Sensor Work?
This sensor measures the power delivered by the motor to the propeller shaft. It typically operates in the range of 6 MW, with precise power measurements across different RPM ranges.
- Benefits of using shaft motor sensor
- The shaft motor sensor optimizes energy use, particularly in systems utilizing waste heat recovery.
- The shaft motor sensor reduces overall energy consumption, contributing to greener maritime operations.
- The shaft motor sensor monitors the efficiency of propulsion, ensuring smooth operations at different speeds.
6:- Thrust Meter
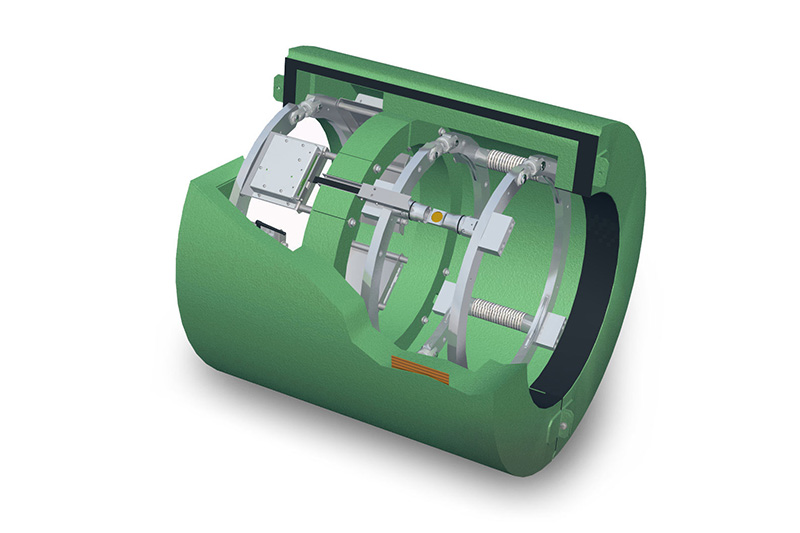
The thrust meter measures the force exerted by the ship’s propeller. The thrust meter is important for understanding how effectively the propulsion system is converting engine power into forward movement.
6.1:- How Does Thrust Meter Work?
The thrust meter measures the rotational speed, torque, and thrust force, using highly sensitive sensors. Unlike torque meters, which focus solely on shaft torque, the thrust meter gives a more comprehensive picture by measuring the actual force applied to the water by the propeller.
6:- Rudder Indicator of Ship
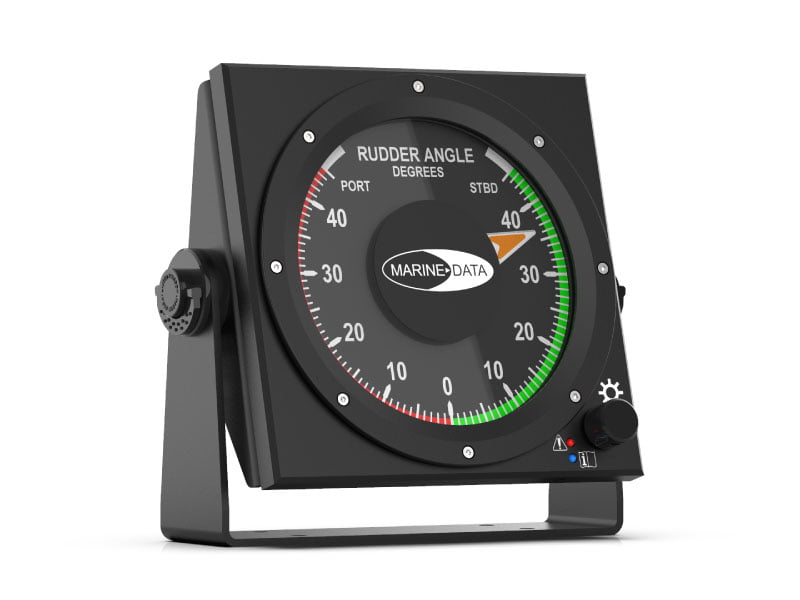

The rudder indicator is essential for steering, providing real-time data on the rudder angle. The Rudder Indicator sensor helps the helmsman and the autopilot system steer the vessel effectively, especially during complex maneuvers in narrow waters or ports.
6.1:- How Rudder Indicator Works?
The rudder indicator continuously measures the angle of the rudder to the ship’s centerline. It’s particularly useful during periods when the rudder direction might shift due to external factors like wind or waves.
- Benefits of using rudder indicator
- Improves navigation accuracy by providing real-time rudder angle data.
- Ensures the vessel maintains a stable course even in challenging conditions.
- Helps prevent over-steering, reducing fuel consumption, and enhance safety.
7:- Stabilizer Fins Sensor
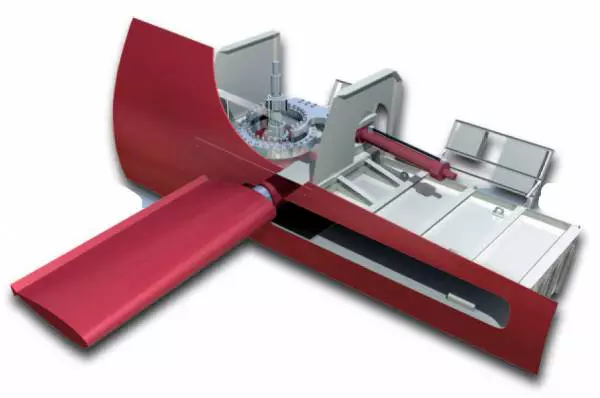
Stabilizer fins are crucial for reducing the rolling motion of a vessel, especially in rough seas. These fins are installed on both sides of the ship and use sensors to continuously adjust their angle to counteract the vessel’s movement.
7.1:- How Stabilizer Fin Sensor Work?
The stabilizer fin sensor monitors the angle of attack of the fins and adjusts them automatically to maintain stability. These sensors help reduce discomfort for passengers and prevent cargo from shifting.
- Benefits of Using Stabilizer Fin Sensor
- The stabilizer fin sensor Enhances comfort during voyages by minimizing rolling.
- Stabilizer fin sensor helps protect sensitive cargo from damage due to excessive movement.
- It Contributes to smoother operations in rough seas, improving crew performance.
8:- Wind Anemometer of Ship
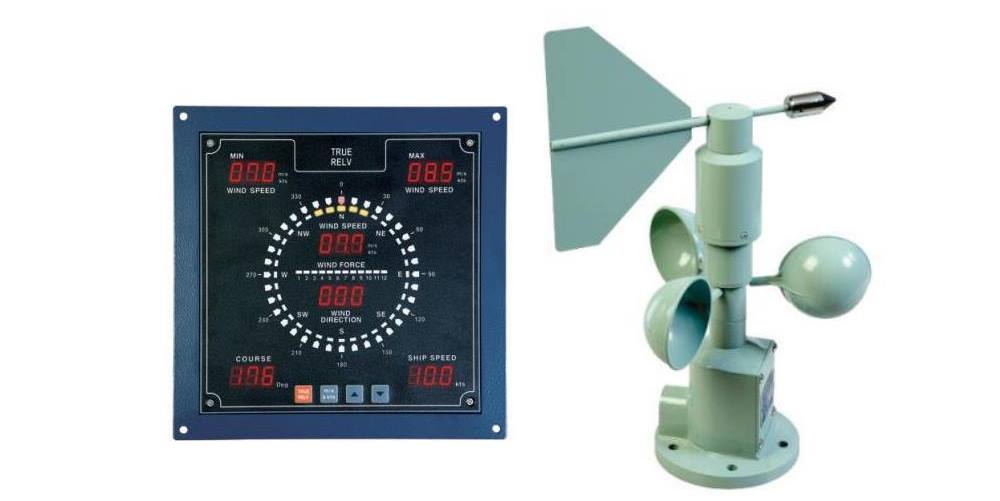

The wind anemometer measures wind speed and direction, providing crucial data for navigation and maneuvering. This sensor is typically placed at the bow or top of the mast to avoid air turbulence caused by the vessel’s structure.
8.1:- How Wind Anemometer Work?
The wind anemometer is equipped with helical blades to measure wind speed and a vane to detect wind direction. It provides real-time data, which is essential for plotting a course, especially in extreme weather conditions.
- Benefits of Wind Anemometer
- Ensures accurate navigation in windy conditions.
- Helps with voyage planning by predicting wind-related challenges.
- Reduces fuel consumption by enabling course adjustments based on wind data.
9:- Global Positioning System (GPS)

The GPS sensor is part of the Global Navigational Satellite System (GNSS) and provides precise positioning, timing, and navigation data to the ship’s crew. GPS is crucial for route planning, navigation, and monitoring the ship’s position relative to its intended course.
9.1:- How Does a GPS Sensor Work?
The GPS sensor uses signals from multiple satellites to calculate the ship’s exact location on Earth. This data is vital for tracking the vessel’s route and ensuring compliance with international maritime laws.
- Benefits of GPS
- Enables accurate route planning and monitoring.
- Helps with collision avoidance by providing precise location data.
- Improves overall safety by integrating with onboard systems for real-time navigation.
10:- Most Common Temperature Sensors
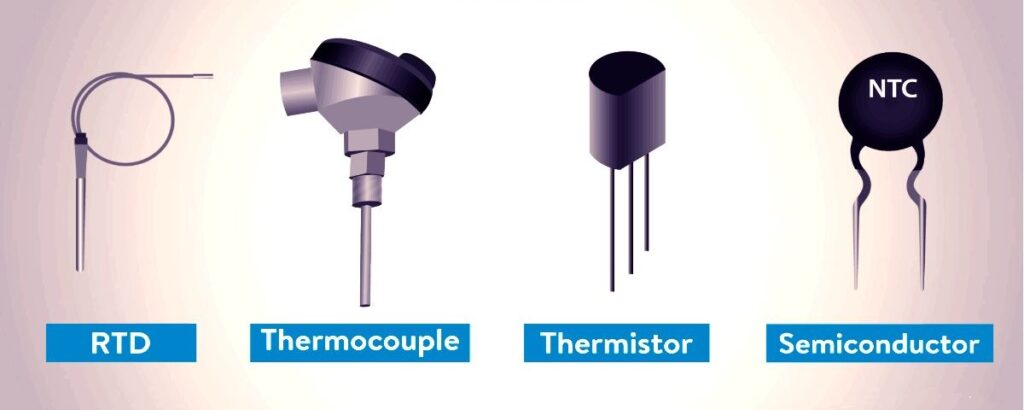

| Sensor Type | Key Features | Best For | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| NTC Thermistor | -Resistance decreases as temperature rises -Very sensitive to small temperature changes | Precision tasks (e.g., medical devices) | – High sensitivity – Cost-effective | – Non-linear output – Needs compensation |
| RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) | – Platinum RTDs are highly accurate – Resistance changes with temperature | Lab equipment & industrial processes | – Very accurate – Stable & repeatable | – Expensive – Slower response |
| Thermocouple | – Two different metals – Generates voltage with temperature change | Wide range temperatures (e.g., furnaces) | – Works over a huge temperature range – Fast response | – Low accuracy – Needs conversion table |
| Semiconductor Sensor | – Integrated into circuits – Linear but less accurate | Basic monitoring (e.g., electronics) | – Simple- Low cost – Linear output | – Lowest accuracy – Slow response |
Quick Tips for Temperature Sensors:
- NTC Thermistor = Precise & Cheap, but Non-linear
- RTD = Super Accurate, but Expensive
- Thermocouple = Wide Range & Fast, but Low Accuracy
- Semiconductor Sensor = Simple & Cheap, but Slow & Less Accurate
11:- Conclusion
- Ship safety and efficiency can be increased with the use of sensors. The RPM and Thrust meters measure the engine performance of the ship, and the Speed Log and Echo Sounder aid in navigation.
- In waves, the stabilizer fins sensor and rudder indicator decrease rolling and enhance steering. Real-time data from the GPS and wind anemometer may be used to assist plan safe routes.
- These sensors aid ships in making wiser judgments, adhering to safety regulations, and using fuel effectively.
Disclaimer :- The opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author and may not necessarily reflect those of Merchant Navy Decoded. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information provided and disclaim any responsibility for it. Data and visuals used are sourced from publicly available information and may not be authenticated by any regulatory body. Reviews and comments appearing on our blogs represent the opinions of individuals and do not necessarily reflect the views of Merchant Navy Decoded. We are not responsible for any loss or damage resulting from reliance on these reviews or comments.
Reproduction, copying, sharing, or use of the article or images in any form is strictly prohibited without prior permission from both the author and Merchant Navy Decoded.


