What is liquefaction? / evaporation / specific volume / critical temperature
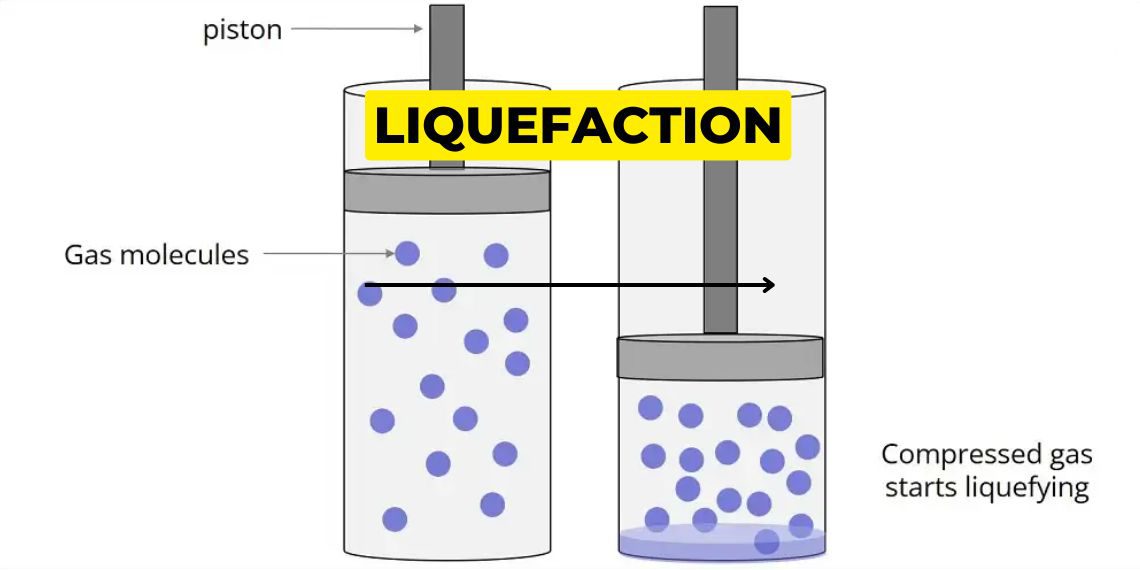
Liquefaction:
Liquefaction is a process of converting gas to liquid. It can be done by two ways:
- By cooling it
- By pressurising it.
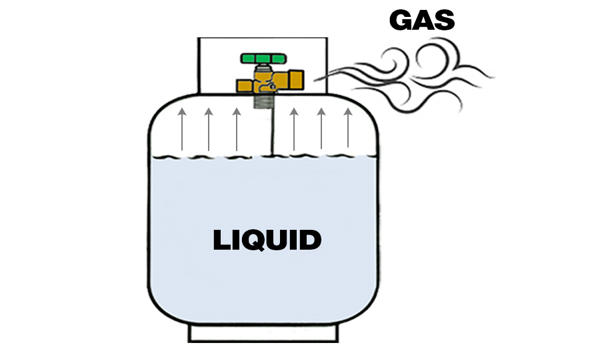
For example; in a home gas cylinder, the gas is stored under high pressure in its liquid form. When the gas is released through the valve, the pressure inside the cylinder decreases, causing the gas to transition from its liquid state to a vapour or gas form. This change occurs as the gas reaches its vapour pressure, which is the point at which the liquid and gas phases coexist in equilibrium. As the gas continues to be used from the cylinder, it remains in its vaporised state until all the gas in the cylinder is consumed.
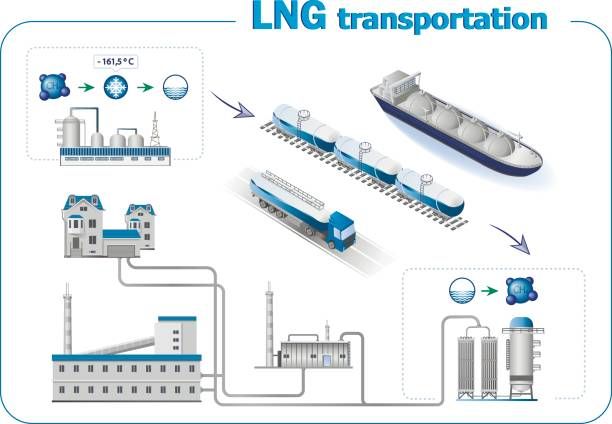
Role of liquefaction in transporting of gases in ship:
Liquefaction indeed plays a crucial role in the transportation of certain gases. It allows gases to be stored and transported more efficiently and economically compared to their gaseous state.
When gases are liquefied, they undergo a phase change from their gaseous form to a liquid form. This process results in a significant reduction in volume, making it much easier to store and transport large quantities of gas in a relatively small space.
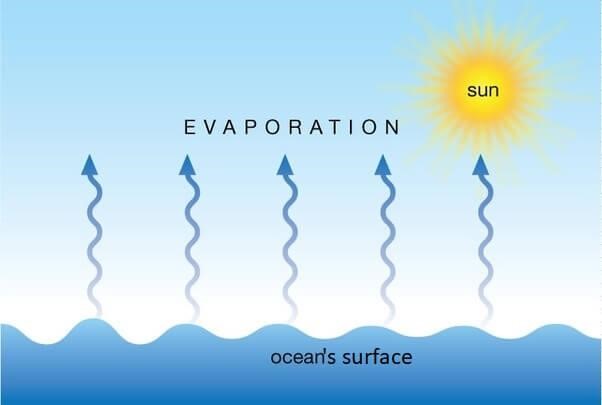
Evaporation:
Evaporation is the process of transforming liquid to gas or vapour form at any temperature. When any type of heat is applied to water or liquid molecules they will gain kinetic energy from the heat and try to break from the outer layer of water which is called evaporation.
The process of evaporation occurs at the liquid’s surface, and it can happen at any temperature below the liquid’s boiling point. Unlike boiling, which is a rapid and intense vaporization that occurs when the entire liquid reaches its boiling point, evaporation is a slower and more gradual process.
Specific volume:
Specific volume is the volume per unit mass of a substance.
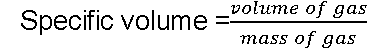
Critical temperature:
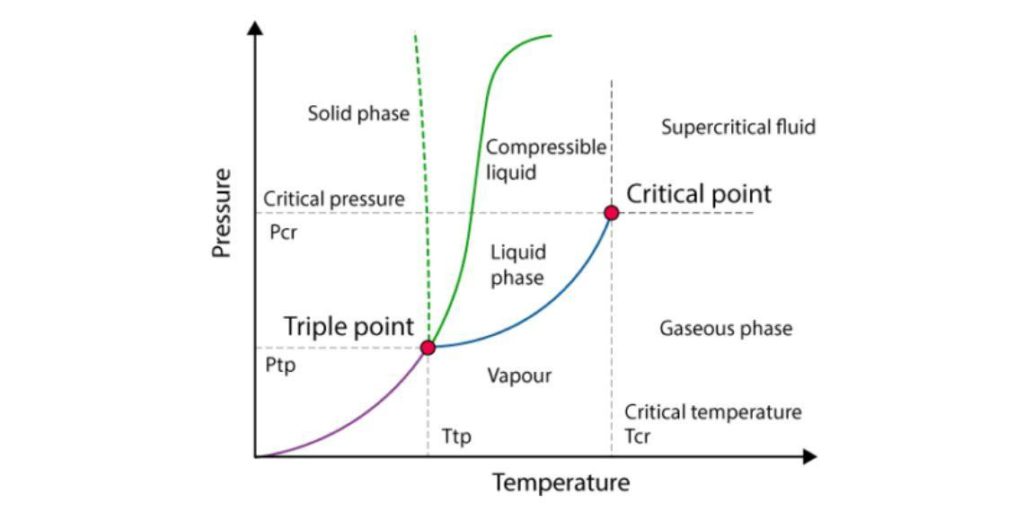
The critical temperature of a substance can be defined as the highest temperature at which the substance can exist as a liquid.
At temperatures above the critical temperature, the substance in its vapour/gaseous state can no longer be liquefied, regardless of the amount of pressure applied to it.
Note:
If you want to learn more about this topic, we suggest checking out our Combo package with the given link https://www.merchantnavydecoded.com/courses/c/ . It’s a great way to dive deeper into the subject through video explanations. This package covers all the important details and presents them in an easy-to-understand format. Watching the videos will help you grasp the topic better and make learning more enjoyable. So, we highly recommend giving our Combo package a try to enhance your knowledge on the subject.
Disclaimer :- The opinions expressed in this article belong solely to the author and may not necessarily reflect those of Merchant Navy Decoded. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information provided and disclaim any responsibility for it. Data and visuals used are sourced from publicly available information and may not be authenticated by any regulatory body. Reviews and comments appearing on our blogs represent the opinions of individuals and do not necessarily reflect the views of Merchant Navy Decoded. We are not responsible for any loss or damage resulting from reliance on these reviews or comments.
Reproduction, copying, sharing, or use of the article or images in any form is strictly prohibited without prior permission from both the author and Merchant Navy Decoded.